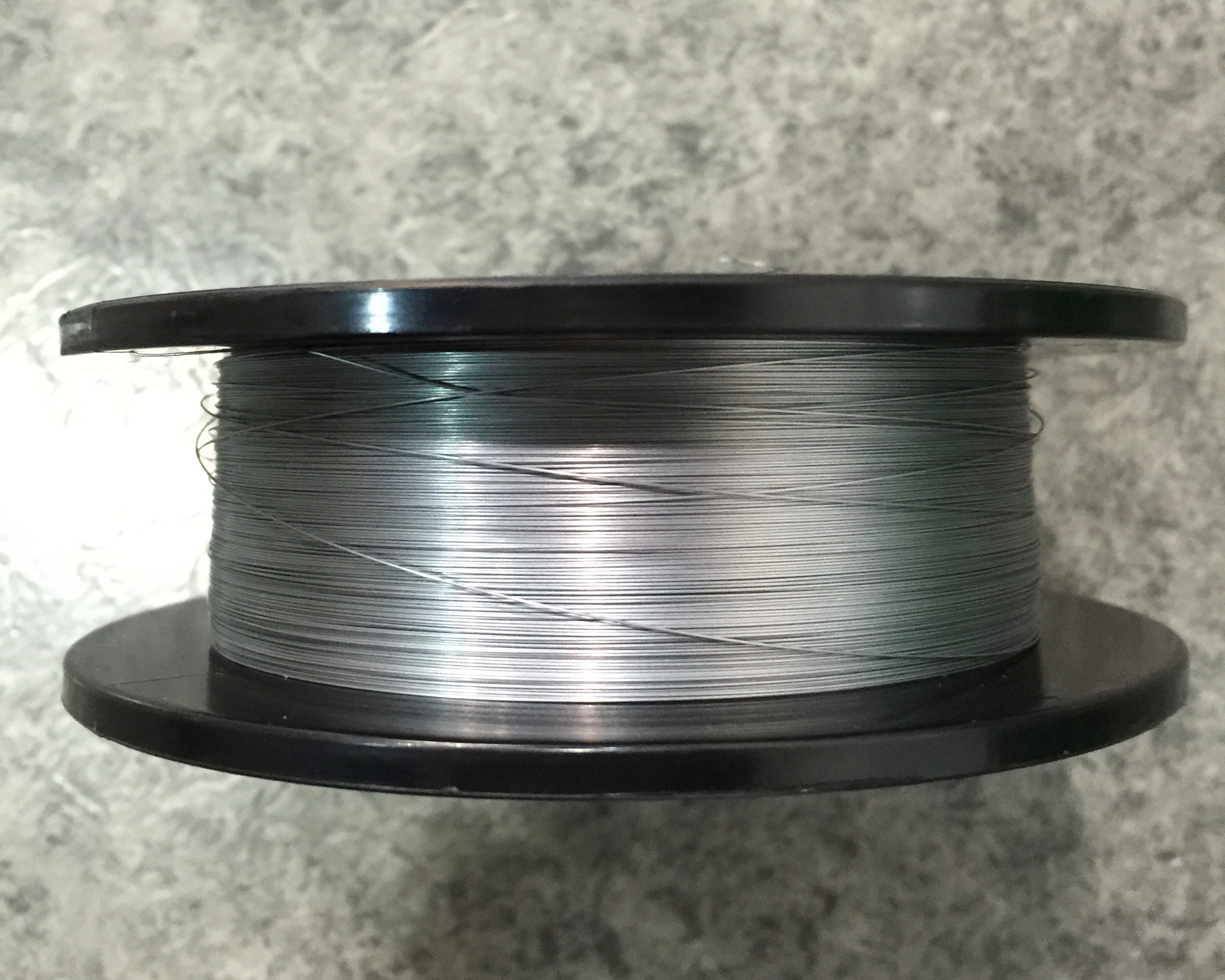
| Product | Niobium Wire (Nb Wire) |
| Part Number | TRM-NB001 |
| Standard | ASTM B392 |
| Material | UNS R04200/ UNS R04210 |
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 |
| CAS Number | 7440-03-1 |
Niobium wire is cold worked from the ingots to the final diameter. The typical working process is forging, rolling, swaging, and drawing. Niobium wire is 0.010 to 0.15 in. in diameter furnished in coils or on spools or reels, and the purity can be up to 99.95%. For the larger diameters, please refer to the Niobium Rod.
Application: The niobium wire is used in arc welding wires for some stabilized grades of stainless steel, and is also used as a material in anodes for cathodic protection systems.
Order Information
Please include the following information with your inquires and orders:
1. Quantity
2. Dimensions
3. R04210 Commercial Grade is the common type. R04200 Reactor Grade is available on request.
Assay
| Element | R04200 (Reactor Grade) | R04210 (Commercial Grade) |
|---|---|---|
| O | 0.015% max | 0.025% max |
| C | 0.01% max | 0.01% max |
| N | 0.01% max | 0.01% max |
| H | 0.0015% max | 0.0015% max |
| Zr | 0.02% max | 0.02% max |
| Fe | 0.005% max | 0.01% max |
| Si | 0.005% max | 0.005% max |
| W | 0.03% max | 0.005% max |
| Ni | 0.005% max | 0.0050% max |
| Mo | 0.01% max | 0.02% max |
| Hf | 0.02% max | 0.02% max |
| Ti | 0.02% max | 0.02% max |
| Ta | 0.1% max | 0.3% max |
| Nb | Remainder | Remainder |
Typical Size Available (Please inquire for details)
| Dimensions | Range | Typical Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | 0.01” -0.124” for wires | +/-0.002” |
| Length | On Request (Straight Or in Coils) | Plus Tolerance |
Please refer to Niobium Rod for larger sizes.
Mechanical Properties – ASTM B392 R04200/R04210
| Diameter | Ultimate Tensile Strength, Min, psi (MPa) | Elongation min % |
|---|---|---|
| 0.020 in. to 0.124 in. | 18 000 (125) | 20 |
Materials available for Niobium and Niobium Alloy Wire
R04200-Type 1—Reactor grade unalloyed niobium,
R04210-Type 2—Commercial grade unalloyed niobium,
R04261-Type 4—Commercial grade niobium alloy containing 1% zirconium.
| Physical properties | Niobium (Atomic#41) |
|---|---|
| Phase | Solid |
| Melting Point | 2750 K (2477°C, 4491°F) |
| Boiling Point | 5017 K (4744°C, 8571°F) |
| Heat of Fusion | 30 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 689.9 kJ/mol |
| Molar Heat Capacity | 24.60 J/(mol•K) |