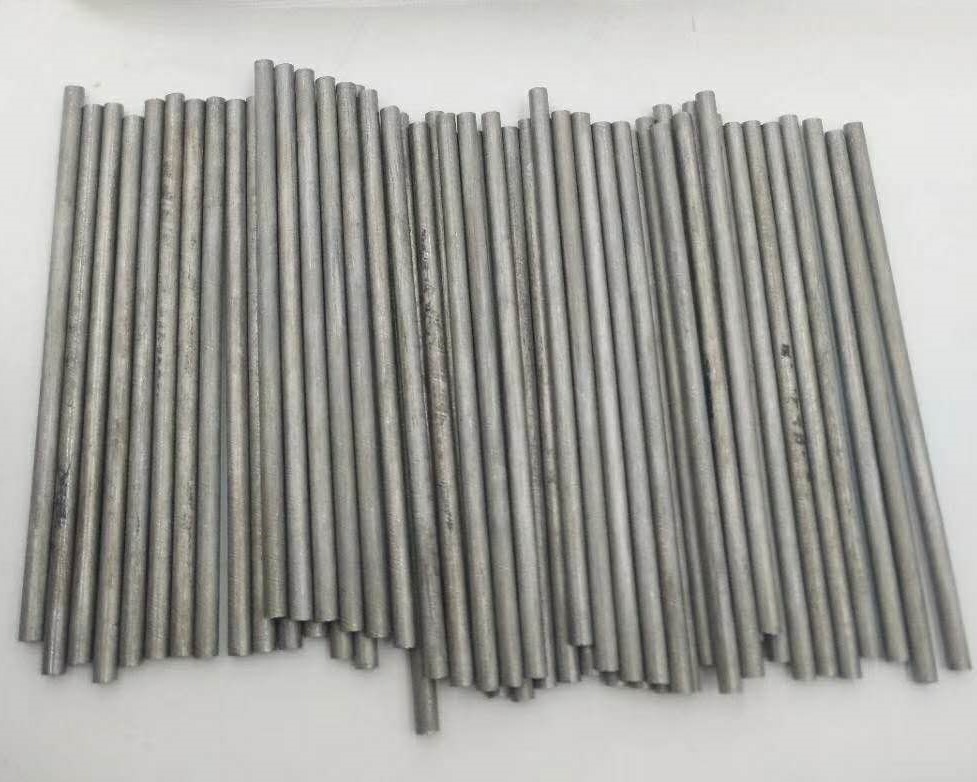
| Product | Niobium Rod (Nb Rod) |
| Part Number | TRM-NB002 |
| Standard | ASTM B392 |
| Material | UNS R04200/ UNS R04210 |
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 |
| CAS Number | 7440-03-1 |
Niobium rod is cold worked from the ingots to the final diameter. The typical working process is forging, rolling, swaging, and machining. Niobium rods 0.12 to 4 in. in diameter are available, and the purity can be up to 99.95%. For smaller diameters, please refer to Niobium Wire.
Application: Niobium rods are used in the fabrication of the corrosion resistant process equipments, including reaction vessels, columns, tube heat exchangers, U-tubes, rupture diaphragms, and etc.
Order Information
Please include the following information with your inquires and orders:
1. Quantity
2. Dimensions
3. R04210 Commercial Grade is the common type. R04200 Reactor Grade is available on request.
Assay
| Element | R04200 (Reactor Grade) | R04210 (Commercial Grade) |
|---|---|---|
| O | 0.015% max | 0.025% max |
| C | 0.01% max | 0.01% max |
| N | 0.01% max | 0.01% max |
| H | 0.0015% max | 0.0015% max |
| Zr | 0.02% max | 0.02% max |
| Fe | 0.005% max | 0.01% max |
| Si | 0.005% max | 0.005% max |
| W | 0.03% max | 0.005% max |
| Ni | 0.005% max | 0.0050% max |
| Mo | 0.01% max | 0.02% max |
| Hf | 0.02% max | 0.02% max |
| Ti | 0.02% max | 0.02% max |
| Ta | 0.1% max | 0.3% max |
| Nb | Remainder | Remainder |
Typical Size Available (Please inquire for details)
| Dimensions | Range | Typical Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | 0.12” -4” | +/-0.03” |
| Length | On Request | Plus Tolerance |
Please refer to Niobium Wire for smaller sizes.
Mechanical Properties – ASTM B392 R04200/R04210
| Diameter | Ultimate Tensile Strength, Min, psi (MPa) | Yield Strength, psi (MPa) | Elongation min % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rod, 0.125 in. to 2.5 in. | 18 000 (125) | 10 500 (73) | 25 |
Materials available for Niobium and Niobium Alloy Rod
R04200-Type 1—Reactor grade unalloyed niobium,
R04210-Type 2—Commercial grade unalloyed niobium,
R04261-Type 4—Commercial grade niobium alloy containing 1% zirconium.
| Physical properties | Niobium (Atomic#41) |
|---|---|
| Phase | Solid |
| Melting Point | 2750 K (2477°C, 4491°F) |
| Boiling Point | 5017 K (4744°C, 8571°F) |
| Heat of Fusion | 30 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 689.9 kJ/mol |
| Molar Heat Capacity | 24.60 J/(mol•K) |